What is 5G?
5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, represents a significant leap forward in mobile communications. It promises faster speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is designed not just for smartphones but for a wide array of applications including IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Evolution from 4G to 5G
While 4G (LTE) revolutionized mobile internet with high-speed data, 5G builds on this by introducing New Radio (NR) technology. Key improvements include enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).

- 1G: Analog voice (1980s)
- 2G: Digital voice and SMS (1990s)
- 3G: Mobile data (2000s)
- 4G: High-speed broadband (2010s)
- 5G: Ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity (2020s)
Key Features of 5G
Speed
Up to 20 Gbps peak data rates, enabling seamless 4K/8K streaming and rapid downloads.
Latency
As low as 1 ms, critical for real-time applications like remote surgery and gaming.
Capacity
Supports up to 1 million devices per square kilometer for IoT ecosystems.
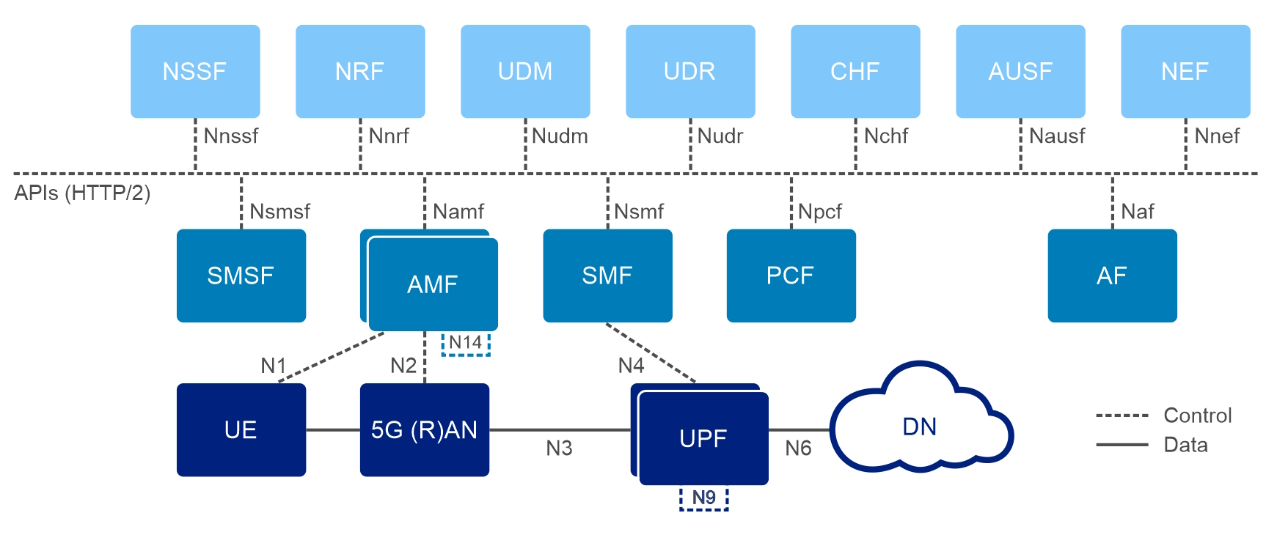
5G Network Architecture
The 5G architecture is service-based, featuring a core network (5GC) that is cloud-native and supports network slicing for customized services.
Use Cases and Applications
5G enables transformative applications across industries:
- Smart Cities: Connected infrastructure for traffic management and energy efficiency.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and remote monitoring.
- Automotive: Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication for safer roads.
- Entertainment: AR/VR experiences with immersive quality.

Challenges and Future of 5G
Despite its potential, 5G faces challenges like infrastructure costs, spectrum allocation, and security concerns. Looking ahead, 5G will evolve towards 6G, focusing on even higher frequencies and AI integration.